1. 二叉树的先序、中序和后序遍历 代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class Solution { private List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList <>(); public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { preorder(root); return ans; } public void preorder (TreeNode root) { if (root!=null ){ ans.add(root.val); preorder(root.left); preorder(root.right); } } public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { inorder(root); return ans; } public void inorder (TreeNode root) { if (root!=null ){ inorder(root.left); ans.add(root.val); inorder(root.right); } } public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { postorder(root); return ans; } public void postorder (TreeNode root) { if (root!=null ){ postorder(root.left); postorder(root.right); ans.add(root.val); } } }
2. 二叉树的层次遍历 2.1 二叉树的层序遍历 给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
思路
广度优先搜索,使用队列保存当前已遍历节点。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { if (root==null ) return new ArrayList <>(); List<List<Integer>> cnt=new ArrayList <>(); Deque<TreeNode> hep=new LinkedList <>(); hep.offer(root); while (!hep.isEmpty()){ int s=hep.size(); List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList <>(); for (int i=0 ;i<s;i++){ TreeNode p=hep.poll(); tmp.add(p.val); if (p.left!=null ) hep.offer(p.left); if (p.right!=null ) hep.offer(p.right); } cnt.add(new ArrayList <>(tmp)); } return cnt; } }
2.2 二叉树的层序遍历 II 给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值 自底向上的层序遍历 。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)。
思路
同题解一,之后再将其反转即可。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom (TreeNode root) { if (root==null ) return new ArrayList <>(); List<List<Integer>> cnt=new ArrayList <>(); Deque<TreeNode> hep=new LinkedList <>(); hep.offer(root); while (!hep.isEmpty()){ int s=hep.size(); List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList <>(); for (int i=0 ;i<s;i++){ TreeNode p=hep.poll(); tmp.add(p.val); if (p.left!=null ) hep.offer(p.left); if (p.right!=null ) hep.offer(p.right); } cnt.add(tmp); } int left=0 ,right=cnt.size()-1 ; while (left<right){ List<Integer> tmp=cnt.get(left); cnt.set(left,cnt.get(right)); cnt.set(right,tmp); left++; right--; } return cnt; } }
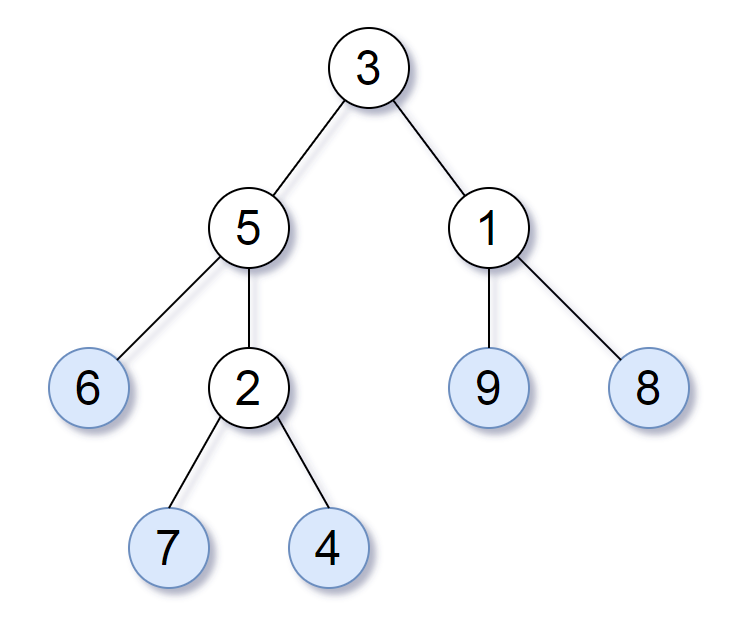
3. 二叉树遍历算法的应用 3.1 叶子相似的树 请考虑一棵二叉树上所有的叶子,这些叶子的值按从左到右的顺序排列形成一个 叶值序列 。
举个例子,如上图所示,给定一棵叶值序列为 (6, 7, 4, 9, 8) 的树。
如果有两棵二叉树的叶值序列是相同,那么我们就认为它们是 叶相似 的。
如果给定的两个根结点分别为 root1 和 root2 的树是叶相似的,则返回 true;否则返回 false 。
思路
深度优先搜索,分别存储两棵树的叶子节点,然后比较。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { private List<Integer> v1=new ArrayList <>(); private List<Integer> v2=new ArrayList <>(); public boolean leafSimilar (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { dfs(root1,v1); dfs(root2,v2); return v1.equals(v2); } public void dfs (TreeNode root, List<Integer> v) { if (root==null ) return ; if (root.left==null &&root.right==null ){ v.add(root.val); return ; } dfs(root.left,v); dfs(root.right,v); } }
3.2 合并二叉树 给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。
想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
返回合并后的二叉树。
注意: 合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
思路
深度优先搜索,依次处理两棵树的对应节点,若其中一棵树节点为null,直接返回另一棵树的节点。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { return dfs(root1,root2); } public TreeNode dfs (TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) { if (root1!=null &&root2!=null ){ root1.val=root1.val+root2.val; root1.left=dfs(root1.left,root2.left); root1.right=dfs(root1.right,root2.right); return root1; }else if (root1==null ){ return root2; }else { return root1; } } }
3.3 二叉树的最近公共祖先 给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科 中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先 )。”
思路
深度优先搜索。
首先判断当前根节点是否为 p 或 q 中的一个,若是则直接返回;
若不是,则递归遍历左右子树;
若左子树返回节点为 null ,则说明左子树中不包含 p 和 q ,返回右子树;
若右子树返回节点为 null , 同左子树情况;
若左右子树返回节点均不为 null , 说明左右子树中分别有 p 和 q ,则当前 root 节点即为最近公共祖先。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root==null ||root==p||root==q) return root; TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q); TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q); if (left==null ) return right; if (right==null ) return left; return root; } }
3.4 二叉树展开为链表 给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
展开后的单链表应该同样使用 TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历
思路
本质上就是将二叉树的左子树移到右子树上,若当前节点左子树不为空,那么将其最右方的节点的下一节点指向当前节点的右节点,这样就将左子树移到了右子树之前;若当前节点左子树为空,则直接继续处理下一个节点即可。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public void flatten (TreeNode root) { TreeNode cur=root; while (cur!=null ){ if (cur.left!=null ){ TreeNode next=cur.left; TreeNode prev=next; while (prev.right!=null ){ prev=prev.right; } prev.right=cur.right; cur.left=null ; cur.right=next; } cur=cur.right; } } }
3.5 二叉树的最大深度 给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
返回它的最大深度 3 。
思路
递归求解左右子树的最大深度。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root==null ){ return 0 ; } int high=Math.max(height(root.left),height(root.right))+1 ; return high; } public int height (TreeNode root) { if (root==null ) return 0 ; int heights=Math.max(height(root.left),height(root.right))+1 ; return heights; } }
3.6 二叉树的最小深度 给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
思路
寻找左右子树的叶子节点,并记录深度,比较得出结果。
注意:与寻找最大深度相比,需要判断是否有叶子节点。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public int minDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root==null ){ return 0 ; } if (root.left==null &&root.right==null ){ return 1 ; } int depth=Integer.MAX_VALUE; if (root.left!=null ){ depth=Math.min(depth,minDepth(root.left)); } if (root.right!=null ){ depth=Math.min(depth,minDepth(root.right)); } return depth+1 ; } }
3.7 二叉树的堂兄弟节点 在二叉树中,根节点位于深度 0 处,每个深度为 k 的节点的子节点位于深度 k+1 处。
如果二叉树的两个节点深度相同,但 父节点不同 ,则它们是一对堂兄弟节点 。
我们给出了具有唯一值的二叉树的根节点 root ,以及树中两个不同节点的值 x 和 y 。
只有与值 x 和 y 对应的节点是堂兄弟节点时,才返回 true 。否则,返回 false。
思路
维护 parent 和 depth 信息,同时设置 flag 标志位标记是否找到目标节点。
最后比较二者的 parent 和 depth 信息。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Solution { boolean flagx=false ; TreeNode xpar; int xdepth; int x; boolean flagy=false ; TreeNode ypar; int ydepth; int y; public boolean isCousins (TreeNode root, int x, int y) { this .x=x; this .y=y; dfs(root,null ,0 ); return xpar!=ypar&&xdepth==ydepth; } public void dfs (TreeNode cur,TreeNode parent,int height) { if (cur==null ){ return ; } if (cur.val==x){ flagx=true ; xdepth=height; xpar=parent; }else if (cur.val==y){ flagy=true ; ydepth=height; ypar=parent; } if (flagx&&flagy){ return ; } dfs(cur.left,cur,height+1 ); if (flagx&&flagy){ return ; } dfs(cur.right,cur,height+1 ); } }
3.8 在每个树行中找最大值 给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值。
思路
广度优先搜索,依次更新每行最大值。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution { public List<Integer> largestValues (TreeNode root) { if (root==null ) return new ArrayList <>(); Deque<TreeNode> hep=new LinkedList <>(); hep.offer(root); List<Integer> cnt=new ArrayList <>(); while (!hep.isEmpty()){ int s=hep.size(); int ans=Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i=0 ;i<s;i++){ TreeNode p=hep.poll(); ans=Math.max(ans,p.val); if (p.left!=null ){ hep.offer(p.left); } if (p.right!=null ){ hep.offer(p.right); } } cnt.add(ans); } return cnt; } }
3.9 找树左下角的值 给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
思路
深度优先搜索,维护一个深度信息,每当找到一个深度大于记录当前深度的节点,修改记录的节点值,并更新当前深度。
由于是左子树先遍历,则到达最底层时,更新为最左边节点的值,然后更新深度,确保不会记录其右边的节点值。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { int ans; int mindepth=-1 ; public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { dfs(root,0 ); return ans; } public void dfs (TreeNode root,int depth) { if (root==null ){ return ; } if (root.left==null &&root.right==null ){ if (depth>mindepth){ mindepth=depth; ans=root.val; } return ; } dfs(root.left,depth+1 ); dfs(root.right,depth+1 ); } }
3.10 对称二叉树 给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
思路
依次递归遍历左右子树,若两个节点不同时为空或者节点值不同,则不对称;反之,继续递归遍历。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { return dfs(root.left,root.right); } public boolean dfs (TreeNode p,TreeNode q) { if (p==null &&q==null ){ return true ; }else if (p!=null &&q!=null ){ if (p.val!=q.val) return false ; else return dfs(p.left,q.right)&&dfs(p.right,q.left); }else { return false ; } } }
3.11 二叉树最大宽度 给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。
树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。
每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些延伸到这一层的 null 节点,这些 null 节点也计入长度。
题目数据保证答案将会在 32 位 带符号整数范围内。
思路
深度优先搜索,每次遍历到当前层的最左侧节点时,记录其编号,然后再递归遍历左右子树,之后再遍历到与当前深度相同的层时,只需将当前节点的编号与记录的最左侧节点的编号相减再加一即得到当前宽度,每次比较取最大值即可得到最大宽度。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { Map<Integer,Integer> cnt=new HashMap <>(); public int widthOfBinaryTree (TreeNode root) { return dfs(root,0 ,1 ); } public int dfs (TreeNode root,int depth,int index) { if (root==null ){ return 0 ; } cnt.putIfAbsent(depth,index); return Math.max(index-cnt.get(depth)+1 ,Math.max(dfs(root.left,depth+1 ,2 *index),dfs(root.right,depth+1 ,2 *index+1 ))); } }
3.12 路径总和 给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
思路
深度优先搜索,递归遍历左右子树,targetSum依次减去当前节点值,当targetSum==0且当前节点为叶子节点时,即找到了目标和。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { return dfs(root,targetSum); } public boolean dfs (TreeNode root,int target) { if (root==null ){ return false ; } if (root.left==null &&root.right==null &&target-root.val==0 ){ return true ; } int val=root.val; return dfs(root.left,target-val)||dfs(root.right,target-val); } }
3.13 二叉树的所有路径 给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
思路
依次遍历到叶子节点,并保存遍历过程中的节点值,当到达叶子节点时,转换为路径并加入目标数组中。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class Solution { List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList <>(); List<String> cnt=new ArrayList <>(); public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) { dfs(root); return cnt; } public void dfs (TreeNode root) { if (root==null ){ return ; } if (root.left==null &&root.right==null ){ tmp.add(root.val); StringBuilder s=new StringBuilder (); for (int i=0 ;i<tmp.size();i++){ s.append(tmp.get(i)); if (i!=tmp.size()-1 ) s.append("->" ); } cnt.add(s.toString()); return ; } tmp.add(root.val); if (root.left!=null ){ dfs(root.left); tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1 ); } if (root.right!=null ){ dfs(root.right); tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1 ); } } }
3.14 路径总和 II 给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
思路
同“路径总和” ,额外使用一个数组存储当前遍历到的节点即可。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution { List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList <>(); List<List<Integer>> cnt=new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { dfs(root,targetSum); return cnt; } public void dfs (TreeNode root,int target) { if (root==null ){ return ; } if (root.left==null &&root.right==null &&target-root.val==0 ){ tmp.add(root.val); cnt.add(new ArrayList <>(tmp)); return ; } tmp.add(root.val); if (root.left!=null ){ dfs(root.left,target-root.val); tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1 ); } if (root.right!=null ){ dfs(root.right,target-root.val); tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1 ); } } }
4. 二叉树的构造 4.1 从前序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 给定两个整数数组,preorder 和 postorder ,其中 preorder 是一个具有 无重复 值的二叉树的前序遍历,postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,重构并返回二叉树。
如果存在多个答案,您可以返回其中 任何 一个。
思路
前序遍历为:
(根结点) (前序遍历左分支) (前序遍历右分支)
后序遍历为:
(后序遍历左分支) (后序遍历右分支) (根结点)
那么找到前序遍历节点在后序遍历序列中的位置,可推知该节点的前面为左右子树,在后序遍历序列中不妨假设从0到该节点位置为左子树,该节点到末尾为右子树,便可由此构造出一棵二叉树。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution { int [] pre; int [] post; int n; public TreeNode constructFromPrePost (int [] preorder, int [] postorder) { Map<Integer,Integer> prem=new HashMap <>(); this .pre=preorder; this .post=postorder; this .n=preorder.length; for (int i=0 ;i<postorder.length;i++){ prem.put(postorder[i],i); } return construct(0 ,n-1 ,0 ,n-1 ,prem); } public TreeNode construct (int p_left,int p_right,int o_left,int o_right,Map<Integer,Integer> cnt) { if (p_left>p_right){ return null ; } if (p_left==p_right){ return new TreeNode (pre[p_left]); } TreeNode root=new TreeNode (pre[p_left]); int num=cnt.get(pre[p_left+1 ]); int size=num-o_left+1 ; root.left=construct(p_left+1 ,p_left+size,o_left,num,cnt); root.right=construct(p_left+1 +size,p_right,num+1 ,o_right,cnt); return root; } }
4.2 根据前序和中序遍历构造二叉树 给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历 , inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历 ,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
思路
前序遍历为:
(根结点) (前序遍历左分支) (前序遍历右分支)
中序遍历为:
(中序遍历左分支) (根结点) (中序遍历右分支)
找到前序遍历节点在中序遍历序列中的对应位置,则其左侧为左子树,右侧为右子树,递归构造即可。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) { Map<Integer,Integer> in=new HashMap <>(); for (int i=0 ;i<inorder.length;i++){ in.put(inorder[i],i); } return construct(preorder,inorder,0 ,preorder.length-1 ,0 ,preorder.length-1 ,in); } public TreeNode construct (int [] preorder,int [] inorder,int p_left,int p_right,int i_left,int i_right,Map<Integer,Integer> in) { if (p_left>p_right){ return null ; } TreeNode root=new TreeNode (preorder[p_left]); int index=in.get(preorder[p_left]); int size=index-i_left; root.left=construct(preorder,inorder,p_left+1 ,p_left+size,i_left,index,in); root.right=construct(preorder,inorder,p_left+size+1 ,p_right,index+1 ,i_right,in); return root; } }
4.3 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
思路
中序遍历为:
(中序遍历左分支) (根结点) (中序遍历右分支)
后序遍历为:
(后序遍历左分支) (后序遍历右分支) (根结点)
找到后序遍历节点在中序遍历序列中的位置,那么其左侧为左子树,右侧为右子树,将后序遍历序列从后往前遍历,即可依次找出根节点。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) { Map<Integer,Integer> in=new HashMap <>(); for (int i=0 ;i<inorder.length;i++){ in.put(inorder[i],i); } return construct(inorder,postorder,0 ,inorder.length-1 ,0 ,inorder.length-1 ,in); } public TreeNode construct (int [] inorder,int [] postorder,int i_left,int i_right,int p_left,int p_right,Map<Integer,Integer> in) { if (p_left>p_right){ return null ; } TreeNode root=new TreeNode (postorder[p_right]); int index=in.get(postorder[p_right]); int size=i_right-index; root.left=construct(inorder,postorder,i_left,index-1 ,p_left,p_left+index-i_left-1 ,in); root.right=construct(inorder,postorder,index+1 ,i_right,p_right-size,p_right-1 ,in); return root; } }
4.4 最大二叉树 给你两个字符串 s 和 goal ,只要我们可以通过交换 s 中的两个字母得到与 goal 相等的结果,就返回 true ;否则返回 false 。
交换字母的定义是:取两个下标 i 和 j (下标从 0 开始)且满足 i != j ,接着交换 s[i] 和 s[j] 处的字符。
例如,在 "abcd" 中交换下标 0 和下标 2 的元素可以生成 "cbad" 。
思路
满足题设字符串的条件:
s 和 goal 的长度相同
s 和 goal 中最多只有两个字母不同
s == goal 时,s 中需要存在一个字母出现次数超过两次及以上,这样在交换的时候才能保证不变。(题目要求交换一次)
s 与 goal 中仅有一个字母不同时,不合题意
s 与 goal 中有两个字母不同时,不妨假设其下标为i,j,则需满足s.charAt(i)==goal.charAt(j)&&s.charAt(j)==s.charAt(i)
满足上述条件即为题设所求。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public boolean buddyStrings (String s, String goal) { if (s.length()!=goal.length()) return false ; if (s.equals(goal)){ int [] chars=new int [26 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<s.length();i++){ chars[s.charAt(i)-'a' ]++; if (chars[s.charAt(i)-'a' ]>1 ){ return true ; } } return false ; }else { int left=-1 ,right=-1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<goal.length();i++){ if (s.charAt(i)!=goal.charAt(i)){ if (left==-1 ){ left=i; }else if (right==-1 ){ right=i; }else { return false ; } } } return (right!=-1 &&s.charAt(left)==goal.charAt(right)&&s.charAt(right)==goal.charAt(left)); } } }
4.5 相同的树 给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的最大二叉树* 。
思路
按照题意进行递归构造,每次寻找当前范围内的最大值。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) { return construct(nums,0 ,nums.length-1 ); } public TreeNode construct (int [] nums,int left,int right) { if (left>right){ return null ; } int index=-1 ,ans=-1 ; for (int i=left;i<=right;i++){ if (nums[i]>ans){ index=i; ans=nums[i]; } } TreeNode root=new TreeNode (ans); root.left=construct(nums,left,index-1 ); root.right=construct(nums,index+1 ,right); return root; } }
4.6 编辑距离 给你两个单词 word1 和 word2, 请返回将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
思路
编辑距离算法。
LeetCode 官方题解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/edit-distance/solutions/188223/bian-ji-ju-chi-by-leetcode-solution/
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int n=word1.length(),m=word2.length(); int [][] dp=new int [n+1 ][m+1 ]; if (n*m==0 ) return n+m; for (int i=0 ;i<=n;i++){ dp[i][0 ]=i; } for (int j=0 ;j<=m;j++){ dp[0 ][j]=j; } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ for (int j=1 ;j<=m;j++){ int left=dp[i-1 ][j]+1 ; int right=dp[i][j-1 ]+1 ; int down=dp[i-1 ][j-1 ]; if (word1.charAt(i-1 )!=word2.charAt(j-1 )) down++; dp[i][j]=Math.min(left,Math.min(right,down)); } } return dp[n][m]; } }
5. 树 5.1 N 叉树的前序遍历 给定一个 n 叉树的根节点 root ,返回 其节点值的 前序遍历 。
n 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
思路
将根节点加入目标数组中,然后依次递归子节点即可。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { List<Integer> pre=new ArrayList <>(); public List<Integer> preorder (Node root) { if (root!=null ){ pre.add(root.val); for (Node p:root.children){ preorder(p); } } return pre; } }
5.2 N 叉树的层序遍历 给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历 。(即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
树的序列化输入是用层序遍历,每组子节点都由 null 值分隔(参见示例)。
思路
广度优先搜索,每次遍历一层。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (Node root) { if (root==null ) return new ArrayList <>(); Deque<Node> hep=new LinkedList <>(); hep.offer(root); List<List<Integer>> cnt=new ArrayList <>(); while (!hep.isEmpty()){ int size=hep.size(); List<Integer> temp=new ArrayList <>(); for (int i=0 ;i<size;i++){ Node p=hep.poll(); temp.add(p.val); List<Node> child=p.children; int cap=child.size(); for (int j=0 ;j<cap&&child.get(j)!=null ;j++){ hep.offer(child.get(j)); } } cnt.add(temp); } return cnt; } }